What causes Bitcoin transaction delays?

A delayed Bitcoin transaction can be both stressful for the recipient and the sender, so it’s important to understand the potential reasons why a Bitcoin transaction could be delayed.
When you send Bitcoin, the transaction may be instantly broadcast to the Bitcoin network, but will not immediately be confirmed. Most wallets, like Luno, require three blockchain confirmations before the transaction can be completed, some may require up to six.
From time to time, due to high volumes, the blockchain may become congested. When this happens, your sends may take some time (up to a few hours) to reach its intended destination. Unfortunately, this is outside of Luno, or any third party’s, control.
How does the blockchain work?
Approximately every ten minutes, a new block is created and added to the blockchain through a process called mining. Each block verifies and records any new transactions (such as the Bitcoin you may be sending). The network then confirms this.
For example, if Sam sends two Bitcoins to Pete, this transaction will remain unconfirmed until the network creates the next block.
Once the next block is created and the new transaction is verified and included in that block, the transaction will have one confirmation.
Approximately every ten minutes after, the transaction is reconfirmed.
What causes delays?
Blocks are usually confirmed approximately every ten minutes.
However, the network can currently only handle a certain amount of transactions per block. Each transaction has a certain size in bytes and each block can only contain a certain number of bytes.
If the network becomes congested and can’t process transactions fast enough, it creates a backlog of unconfirmed transactions. The network eventually resolves everything within a day or so.
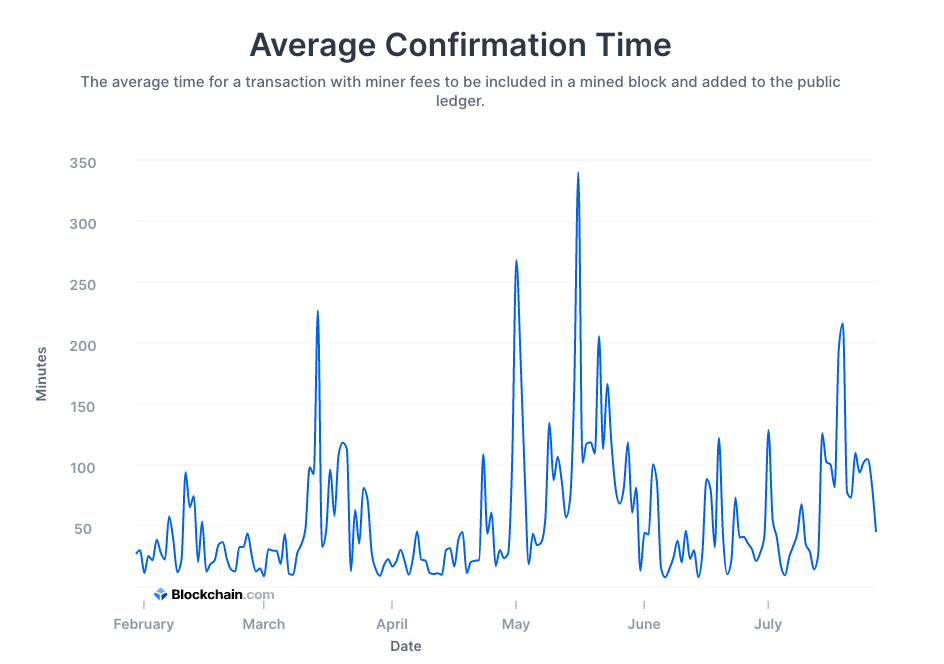
You’ll notice the variations in the average confirmation time in the graph below.
Is there a faster alternative?
Bitcoin is an evolving technology, and there is an ongoing discussion of the “block size debate”, which aims to address these problems. Transaction speeds will improve in the future if the network implements changes.
Fortunately, we have another option for Luno customers. You can send cryptocurrency to other Luno customers using their email address or phone number instantly and for free!
 Discover
Discover Help Centre
Help Centre Status
Status Company
Company Careers
Careers Press
Press